Inject a certain amount of nitrogen (nitrogen foam) into the oil well in a short time, and then shut in the well for a period of time. After the nitrogen diffuses to the reservoir, use nitrogen: gravity differential displacement, expansion energy displacement, and water pressure cone.
Replace the remaining oil in relatively high structural areas and microcracks to achieve the goal of increasing crude oil production.
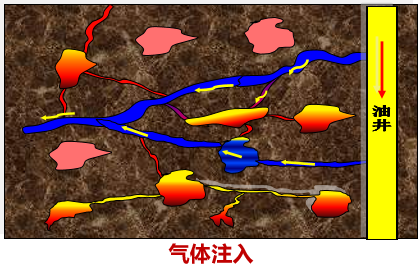
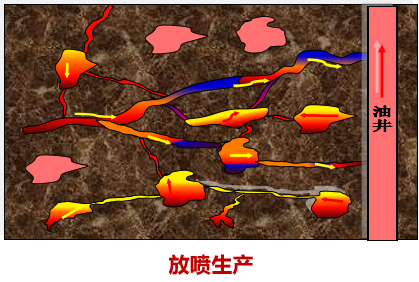
The compression coefficient of nitrogen is high, and injecting nitrogen can effectively supplement the energy of the formation. At the same time, nitrogen partially dissolves in crude oil and has a certain expansion and viscosity reduction effect.
Nitrogen has inert chemical properties, is safe and reliable, has a wide range of sources, is inexpensive, and is easy to apply on site.
Nitrogen migrates towards the top of the reservoir and can displace difficult to use attic oil through gravity differentiation.
Nitrogen gas has a gas resistance effect in oil reservoirs, making it easier for gas to enter low-permeability layers, increase sweep efficiency, and displace bound oil into movable oil.
Plugging and profile control function: foam enters the high permeability layer first. Due to Jamin effect, the flow resistance will gradually increase. With the increase of injection pressure, foam can enter the low permeability layer in turn to improve the sweep efficiency. At the same time, it can enter and fill the pores of various structures, drive out the discontinuous residual oil, and improve the microscopic sweep efficiency;
Improving oil displacement efficiency: It can significantly reduce the interfacial tension between oil and water, increase the wetting angle of the sample surface during oil testing, which is beneficial for improving oil displacement efficiency;
Improve reservoir energy: Injected nitrogen can supplement reservoir energy and increase reservoir pressure.
Oil displacement mechanism:
In view of the limited precipitation effect of single nitrogen bubble foam flooding in high water cut well group, it is necessary to explore and carry out tests of multiple technology combinations (such as plugging agent, microsphere flooding test, etc.).
Elastic microspheres are in a discontinuous dispersed state in aqueous solution and have the characteristics of nanometer and micrometer scale. Due to the inherent elastic deformation ability of elastic microspheres, this characteristic determines that they are subjected to displacement force in porous media and compression deformation at the throat, achieving breakthrough forward migration. This system forms a high-strength viscoelastic system with the triple functions of "regulating, blocking, and driving".


